Introduction to Wire Harness Design
In this guide to wire harness design, development, and manufacturing, we’ll start with the basics and move through the process of manufacturing. First, understand what a wire harness is, then we’ll discuss the steps involved in designing them. We’ll review components and materials, followed by a discussion of the options for purchasing them. Lastly, we’ll how automation is influencing wire harness manufacturing.
What is a Wire Harness, and What are the Benefits?
A wire harness is a set of cables, wires, and connectors connecting electrical components in an electronic device. It is a crucial component of any electronic system and can be custom designed for specific applications. A wire harness helps simplify the wiring process by reducing the number of cables needed and providing an easy way to connect components.
Theyoffer many benefits, including improved reliability, reduced installation time, safety, and cost savings. Typically, due to being application-specific, wiring harnesses are custom designed, tailoring them for maximum efficiency and performance. Different types of wire harnesses are available depending on the application, such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial. With the help of advanced design tools, designers can quickly create custom wire harnesses with high accuracy and precision.
The Step-by-Step Process for Designing and Developing a Wiring Harness
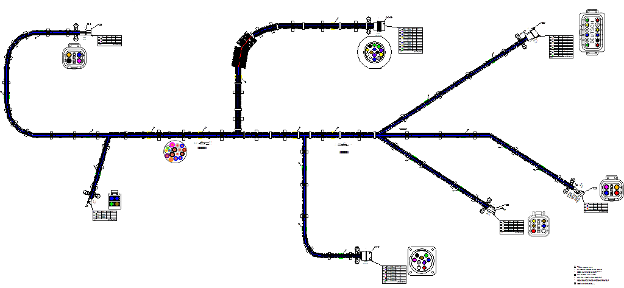
The process of designing and developing a wiring harness involves several steps, starting with gathering information about the requirements and specifications of the wire harness. The next step is creating a schematic or wiring harness diagram, followed by selecting the appropriate components and materials. The actual design of the harness involves laying out the wires, connectors, and other elements in a specific configuration. Next, testing the wiring harness ensures that it meets the required performance criteria. Finally, the completed harness is inspected and tested before installation in the final product. This step-by-step process ensures the design and development of the wire harness meet the requirements and specifications of the final product.
Wire Harness Components and Materials Used in Manufacturing
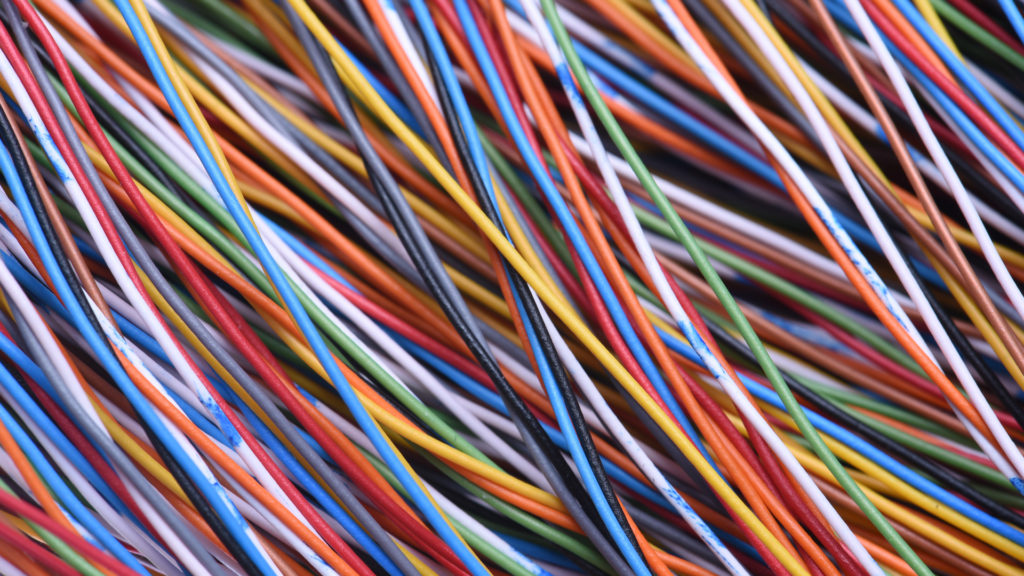
Wire harnesses consist of various components and materials in the manufacturing process. The most common elements include wires, connectors, terminals, and protective sleeves. Wires are typically made from copper or aluminum and are coated with insulation to prevent electrical interference. Connectors join wires and come in various shapes and sizes depending on the application. Terminals are attached to the wire ends to connect them to other components. Protective sleeves to cover the cables provide additional protection from heat, moisture, and other environmental factors.
The materials used to manufacture wire harnesses can vary depending on the application and harness assembly requirements. Common materials include PVC, polyethylene, and polypropylene for insulation and nylon or polyester for protective sleeves. With specific applications where high temperatures or extreme environmental conditions are a concern, using more advanced materials such as Teflon or silicone is common.
Overall, selecting wire harness components and materials is critical to ensuring the harness performs reliably and meets the required specifications. Manufacturers must carefully consider the application and environment of the wiring harness to determine the appropriate components and materials.
Advantages of Purchasing Pre-Made Wire Harnesses vs. Custom Solutions
The two main options for wire harnesses are pre-made and custom solutions. While custom solutions offer more flexibility and customization options, pre-made harnesses have several advantages that make them popular for many applications.
One significant advantage of pre-made wire harnesses is cost-effectiveness. Manufacturers typically mass-produce pre-made harnesses, enabling them to manufacture them at a lower cost than custom solutions. As a result, this can significantly benefit smaller production runs or applications with tight budget constraints.
Pre-made wire harnesses offer faster lead times and shorter production times. Since pre-made harnesses are already manufactured and available for purchase, they can be shipped out quickly and installed in the final product with minimal delay. With shorter lead times, this can be particularly beneficial for applications with tight production schedules or where downtime is not an option.
Designers and manufacturers typically create pre-made wire harnesses to meet industry standards and regulations, providing an additional advantage. Therefore, it ensures that the harness meets the necessary safety and performance requirements for the application. On the other hand, custom solutions may require additional testing and certification to ensure compliance with industry standards.

In summary, pre-made wire harnesses offer several advantages over custom solutions, including cost-effectiveness, faster lead times, and compliance with industry standards. While custom solutions may be necessary for some applications, pre-made harnesses are a reliable and efficient option for many applications.
How Automation is Revolutionizing Wiring Harness Manufacturing
Manufacturing wiring harnesses has traditionally been labor-intensive and time-consuming, but automation is revolutionizing the industry and improving efficiency and productivity. Automation involves using robotic systems and computer-controlled machines to perform traditionally manual tasks.
One use of automation in manufacturing wiring harnesses is through automated wire-cutting and stripping machines. These machines can cut and strip wires with high accuracy and speed, reducing the time and labor required for these tasks.
The use of automated assembly systems is streamlining the production of wiring harnesses. These systems use robots and other machines to assemble wires, connectors, and other components into the final harness. By automating the assembly process, manufacturers can reduce the risk of errors and improve overall production efficiency.
Another way that automation is revolutionizing the manufacturing of wiring harnesses is through the use of data analysis and monitoring. Manufacturers can identify areas to improve and optimize production to reduce waste and increase efficiency by collecting and analyzing production processes and performance data.

Overall, the use of automation in manufacturing wiring harnesses is improving efficiency, reducing labor costs, and improving the overall quality of the final product. As automation technology advances, it will continue to play an increasingly important role in the industry’s future.
Conclusion
A wire harness is a critical component in electronic systems that offers many benefits. Custom wiring harnesses are designed using advanced tools, and the process involves several steps, including selecting appropriate parts and materials. Pre-made wire harnesses offer advantages such as cost-effectiveness, faster lead times, and compliance with industry standards. Automation is revolutionizing the manufacturing of wiring harnesses, improving efficiency and productivity. As automation technology advances, the industry can expect to see even more significant improvements in the future.
Next Steps for Your Wire Harness Design Journey
Discover how Zuken’s Wire Harness Design solutions can help you improve your wire harness design process
Related Products and Resources

- Products
Enable connected and automated wire harness design and manufacturing environments
- Software Evaluation
E3.series Test-Drive provides a web-based training course that guides you through the creation of a real life design example with E3.series using E3.cable and E3.panel

- Webinar
This webinar covers the logical part of the wire harness design process consisting of creating the wiring diagram and the topology design.



