Even though there have been many helpful changes in the technology for harness assemblies, issues persist with building the harness itself. Wood frames, nails, multiple boards, and paper instructions are the traditional tools used to assemble cable harnesses. However, an innovative partnership between Zuken and Delta Sigma revolutionizes the entire process with augmented reality for wire harness assembly.

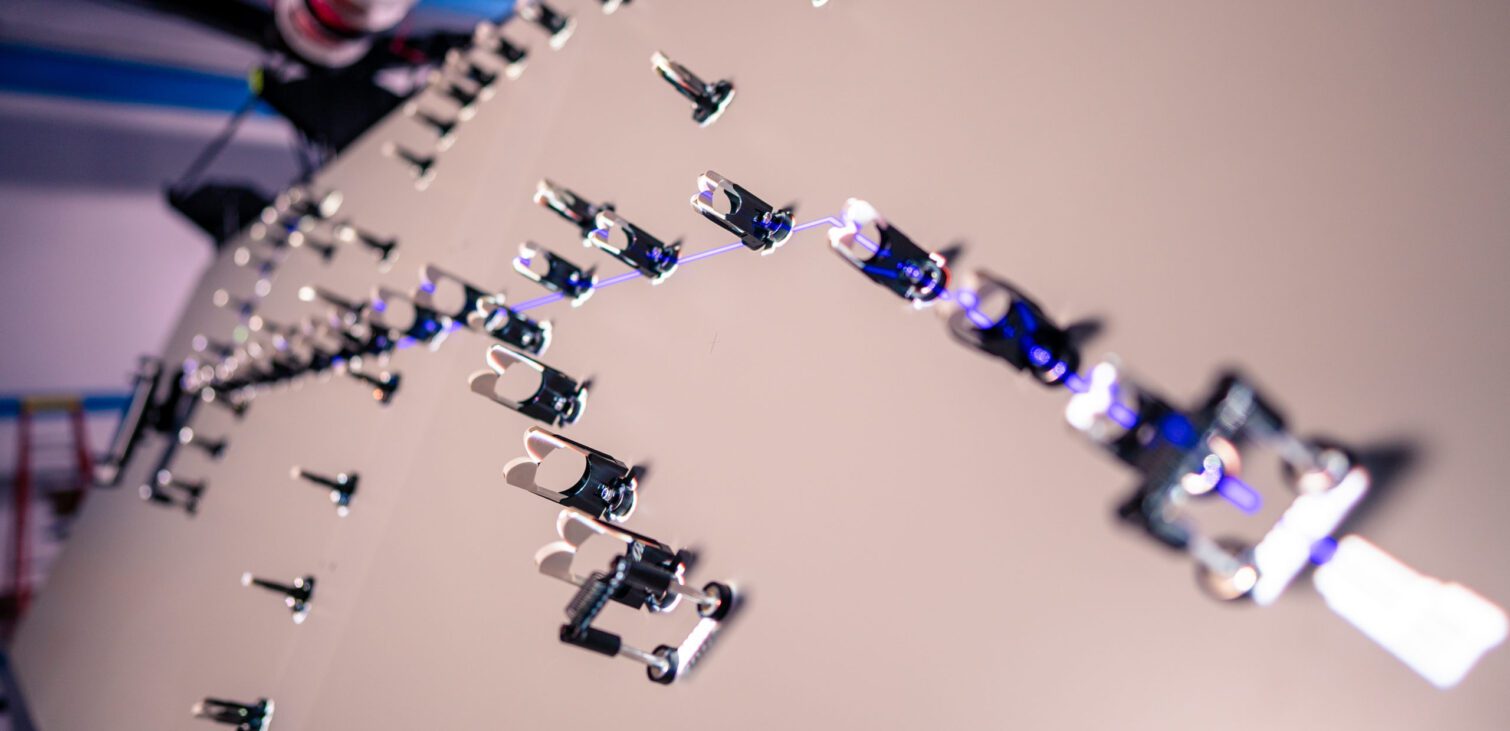
Combining the Zuken digital ecosystem with Delta Sigma’s HarnessWorks augmented reality, as shown in Figure 1, can solve many common wire harness assembly problems. At the same time, the companies address the issues and goals most cable harness manufacturers face. But how does it work?
Shared Goals and Challenges of Wire Harness Designers and Manufacturers
No one will argue that the accurate, high-production assembly of wire harnesses can be challenging. With cumbersome assembly boards, complex paper instructions and line changes, technicians often find themselves frustrated and their productivity hampered during the assembly process.
Outdated technology can lead to problems such as low productivity, the inability to implement manufacturing successfully, and persistently high overhead costs. However, switching to cutting-edge software is not the complete answer. Leveraging the software in the service of overcoming production challenges and helping manufacturers reach their goals is a must.
Wire harness manufacturers often focus on reducing costs and improving margins, increasing manufacturing productivity, reducing errors and improving quality, and reducing waste and re-work. To achieve these goals, many manufacturers attempt to reduce design overhead, implement intelligent manufacturing, adopt design-for-manufacturing principles, and implement just-in-time manufacturing capabilities.
Using augmented reality – with Zuken’s digital ecosystem – is a path to reaching these critical manufacturing goals. Let’s take a look at how this all comes together.
The Traditional Approach to Wire Harness Manufacturing and Assembly: A Fraught System
In traditional wire harness manufacturing, wood frames, nails, and complex paper instructions help guide assembly technicians. Assembly may require multiple boards, while line changes mean a further reduction in production and even more complicated instructions.
Once a particular harness assembly is complete, the harness frames/boards go into storage for reuse, which can take up costly space and make it challenging to find the right board later. In addition, introducing changes to a design means existing wire harness boards require careful modification or a new build from scratch. Either approach can easily lead to errors, which involves reworking harnesses and lost productivity.
Industrial Augmented Reality for Wire Harness Assembly
Augmented reality superimposes a computer-generated image onto a user’s view of the physical world, not unlike a HUD (Heads-Up Display). For example, in an industrial setting, it can label objects in someone’s view, provide instructions, demonstrate assembly, or show operating conditions for different pieces of equipment. However, unlike virtual reality, augmented reality adds information to a user’s real-world view instead of replacing that view.
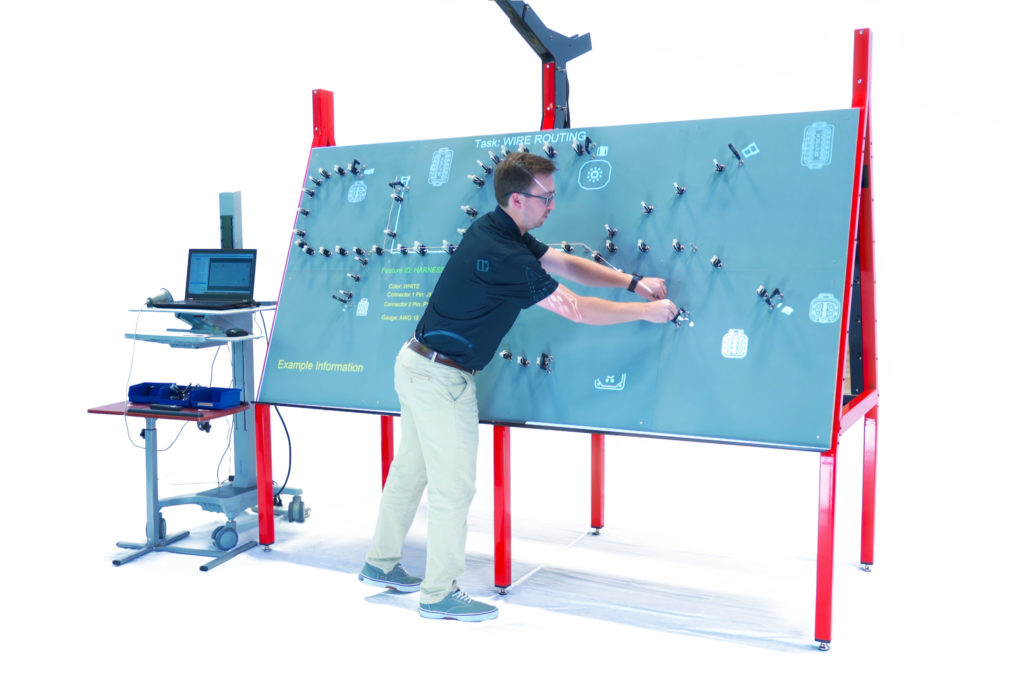

In the context of wire harness assembly, augmented reality provides step-by-step instructions projected directly onto a reusable harness board, as illustrated in Figure 2. Nails and pegs are replaced with configurable magnetic accessories, and the traditional wood frame becomes powder-coated steel. Designers can reconfigure their harness designs in software and export them to the augmented reality tool, making changes easier to implement and thus minimizing errors in layout.
Implementing Augmented Reality for Your Wire Harness Assembly and Manufacturing
We talked a bit above about some of these critical goals for manufacturers:
- Reduce design overhead
- Drive intelligent manufacturing
- Adopt design-for-manufacturing principles
- Implement just-in-time manufacturing principles
Let’s consider how augmented reality can help manufacturers achieve those goals.
First, replacing non-reusable physical harness boards with reconfigurable harness layout boards reduces design overhead significantly through reusability and reduced (often expensive) storage requirements.
Next, Intelligent manufacturing focuses on processes that combine flexible and reconfigurable smart manufacturing processes. Augmented reality supports reconfigurable designs through intelligent, optimized, and automated changes to the instructions and wire harness assembly overlay by simply importing the new design.
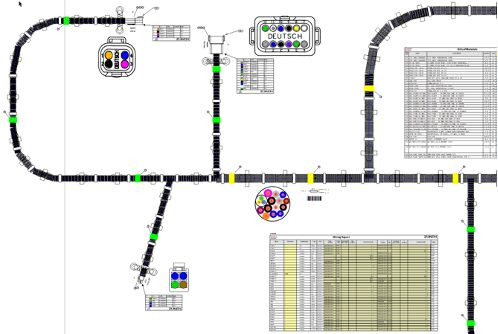
Augmented reality, combined with a wire harness ecosystem, also supports a flexible approach to wire harness manufacturing, as shown in Figure 3. The result is easy and cost-effective manufacturing of everything from customized one-off harnesses to long production runs.
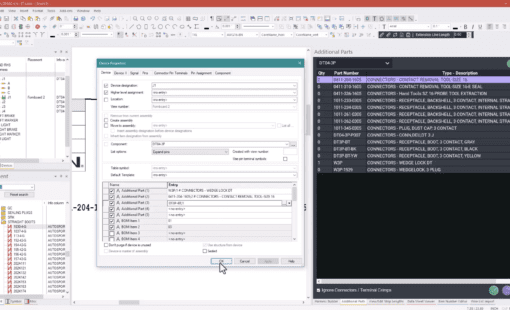
Adopting DFM (Design For Manufacturing) requires implementing industry practices that support the easy manufacture of products. Augmented reality simplifies the wire harness assembly process, increases manufacturing productivity, and reduces errors.
Implementing just-in-time manufacturing principles enables manufacturers to quickly switch from one product to another without significant delays or challenges. Augmented reality for wire harness assembly does this through easily reconfigured layout boards and the ability to simply choose the design in use.
HarnessWorks Augmented Reality
Zuken already has an extensive suite of tools for electrical harness design, E3.series., Zuken has partnered with Delta Sigma to leverage HarnessWorks with E3.series design tools to add value. This duo creates an innovative augmented reality approach to dynamic design-to-manufacturing harness production.
HarnessWorks provides assisted automation for wire harness assembly through step-by-step augmented reality instructions projected onto a harness board. In addition, it provides managers with insight into production real-time activity dashboards and long-term data for analyzing trends.
HarnessWorks also extends the digital thread related to wire harnesses, which has become extremely important in BIM (Building Information Management) and digital twinning. Importing digital files from wire harness design software into HarnessWorks results in simplified, step-by-step instructions and an augmented assembly overlay.
Conclusion
When combining HarnessWorks with E3.series wire harness and design manufacturing ecosystem, the result is a digital design system that uses the latest methods to seamlessly support harness manufacturers’ goals from concept through assembly.
Related Products and Resources

- Blog
- Blog
- Blog

- Blog