Introduction to Engineering Data Management (EDM)
In today’s fast-paced technological world, engineering data management (EDM) has become a cornerstone for successful project execution in various engineering fields. Specifically, engineering data management is a systematic approach to acquiring, validating, storing, protecting, and processing required data to ensure its accessibility, reliability, and timeliness for its users.
The Importance of EDM
EDM is vital for several reasons. It enhances collaboration among team members, ensures data integrity, and aids in decision-making processes. Moreover, by effectively managing data, companies can avoid costly errors, meet compliance standards, and maintain a competitive edge in the industry. In production environments, engineering data management facilitates the efficient use of resources and streamlines manufacturing processes, ensuring that production aligns with design specifications. Additionally, the ability to easily access version history through EDM systems allows for better tracking of changes, aids in quality control, and supports effective audit trails, making it invaluable for continuous improvement and compliance with industry standards.

The 4 Types of Data Management
- Data Governance: Setting data management policies.
- Data Stewardship: Overseeing data policy implementation.
- Data Architecture: Structuring data systems.
- Data Analytics and Quality: Ensuring data accuracy and analysis readiness.
Key Components of EDM
- Data Acquisition and Validation: This involves collecting data from various sources and ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
- Data Storage and Protection: Storing data securely and protecting it from unauthorized access and potential data breaches is crucial.
- Data Processing and Usage: This refers to processing data into a usable form and applying it effectively in engineering projects.
EDM in Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
EDM and PLM are complementary players in the Product Lifecycle. Engineering data management is engineering-facing and provides engineering organizations with a secure and flexible data management system during design. Data is stored in the design tool’s native format, providing better design history and traceability. Design changes are frequent at this phase, and an engineering-facing tool dramatically boosts efficiency and product. Also, it is worth noting that the EDM system relies on the PLM system for critical supply chain information consumed and delivered to the engineer by the EDM system.
PLM is manufacturing-facing. A hand-off occurs as the product design matures and is ready for manufacturing. The EDM system executes a release-to-manufacturing process, generating and delivering the documents necessary for manufacturing. At this point, the PLM system takes over. The manufacturing release package is traceable to a specific EDM version, providing critical traceability.

EDM in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
EDM integrates technical data with business processes in ERP systems, aligning engineering with financial, procurement, and supply chain operations.
Engineering Data Management in PCB Design
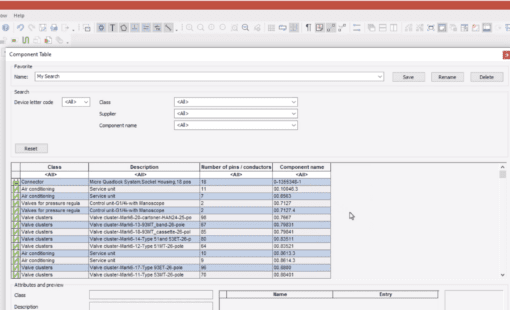
In the realm of PCB design, EDM’s role is crucial. It ensures that all components and layouts are accurately documented and accessible. Managing the many versions and iterations of a PCB design, EDM helps avoid errors, reduce time-to-market, and improve product quality while fostering collaboration among various teams.
Engineering Data Management in Electrical Design
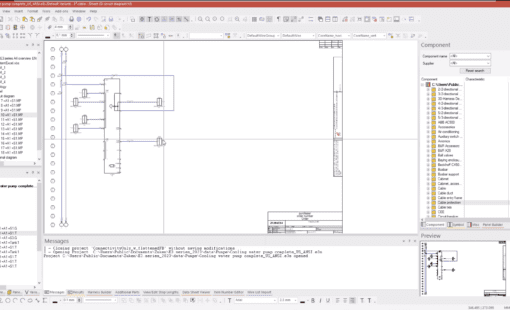
Similarly, in electrical design, EDM is indispensable. It manages complex schematics, components, and compliance with safety standards. Furthermore, by providing a centralized data repository, EDM ensures consistency and accuracy throughout a project’s lifecycle, streamlining report generation and ensuring adherence to industry standards.
Challenges
As products become more complex, engineering data management is more critical than ever. Consequently, product complexity is driving the adoption of model-based design; this is a shift from documents to models built on relationships and creates a profound change in the design process that will challenge the entire product life cycle.
Future Trends
The future of engineering data management is promising, with trends like the integration of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and advanced analytics. These technologies enhance data processing capabilities and provide more insightful and actionable data for engineering projects.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
In conclusion, engineering data management is not just about handling data; it’s about creating a foundation for innovation and efficiency in engineering projects. As we move forward, EDM will continue to evolve, embracing new technologies and methodologies to meet the ever-changing demands of the engineering world.
Related Products and Resources

- Products
The traditional practice of mechanical, electrical and electronic engineers working in silos – then consolidating efforts late in the development process – is no longer viable for successful companies. Zuken offers a portfolio of scalable domain data management solutions for PCB and electrical/fluid design plus a range of solutions that integrate design and domain data management into the PLM and ERP world.

- Products
Zuken’s engineering data management platform DS-CR has been created to support the specific demands of PCB design data management. It combines multi-site library, design data and configuration management into a unified engineering environment.
- Brochure

- Brochure